Lighting Model-Guided Initialization for Gradient Descent-Based Projector Compensation
Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology
IEEE Access
Abstract
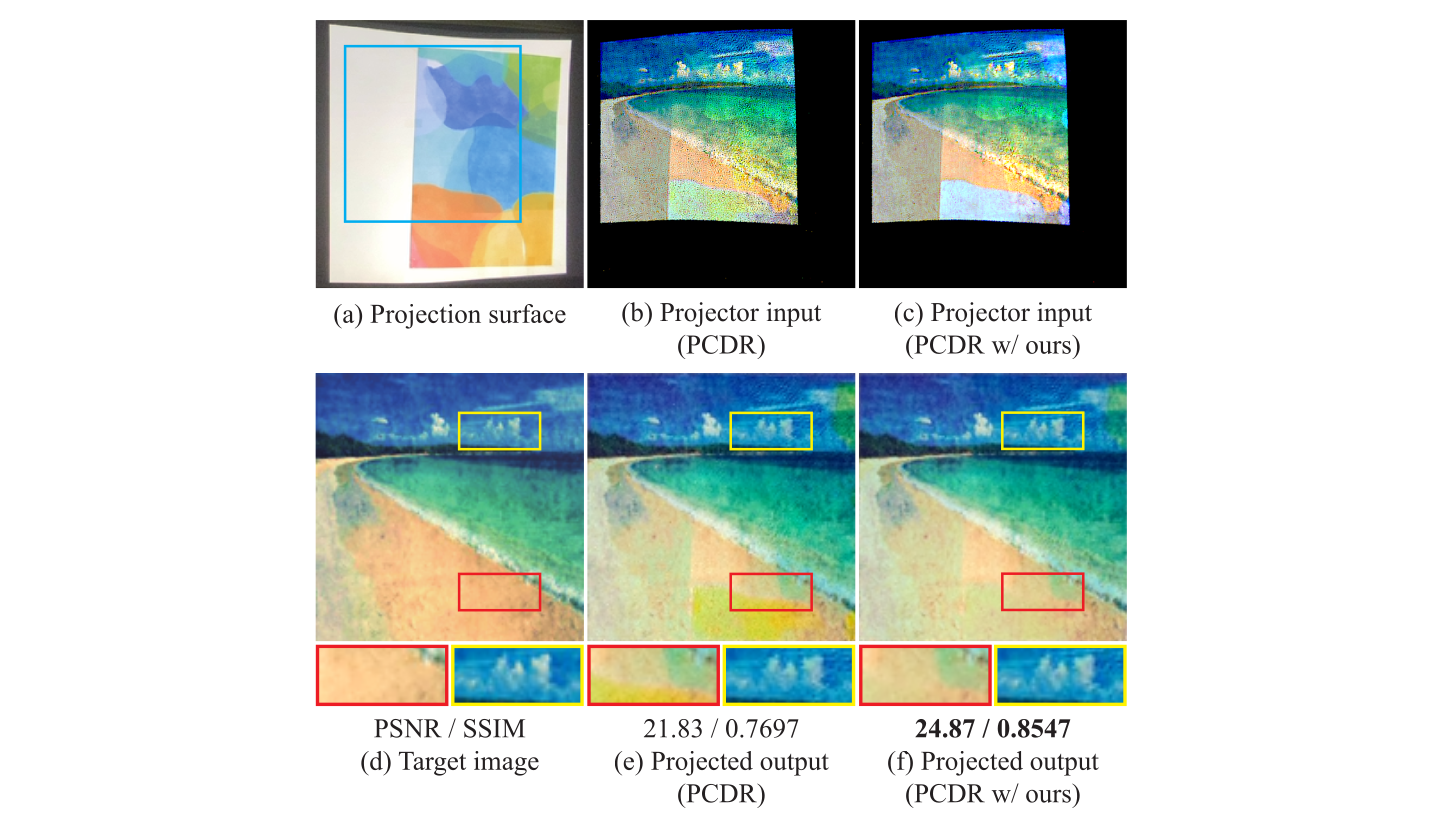
Projection mapping, which maps a projector input (i.e., an image) onto a physical surface, is widely used to display user-specified visual content. However, the projected content can become distorted when an ideal surface, such as a flat and white plane, is unavailable. As a result, adjusting the projector input using a projector compensation technique becomes necessary to ensure that the projected image matches the user-provided target image. While various techniques have been proposed for projector compensation, a recent approach models projection mapping as a simulatable process in virtual space, where a light transport algorithm simulates the projection mapping. In such rendering frameworks, projector compensation is typically achieved by iteratively adjusting the projector input via a gradient descent-based optimizer, starting from an initial guess (often chosen arbitrarily). In this paper, we investigate how to set the initial values more effectively rather than choosing them arbitrarily. As the main contribution of the paper, we propose a new initialization scheme that determines the starting values based on a lighting model. We then integrate this model-guided initialization into gradient descent-based optimization and demonstrate that it improves projection mapping results, particularly for non-planar and colored surfaces.